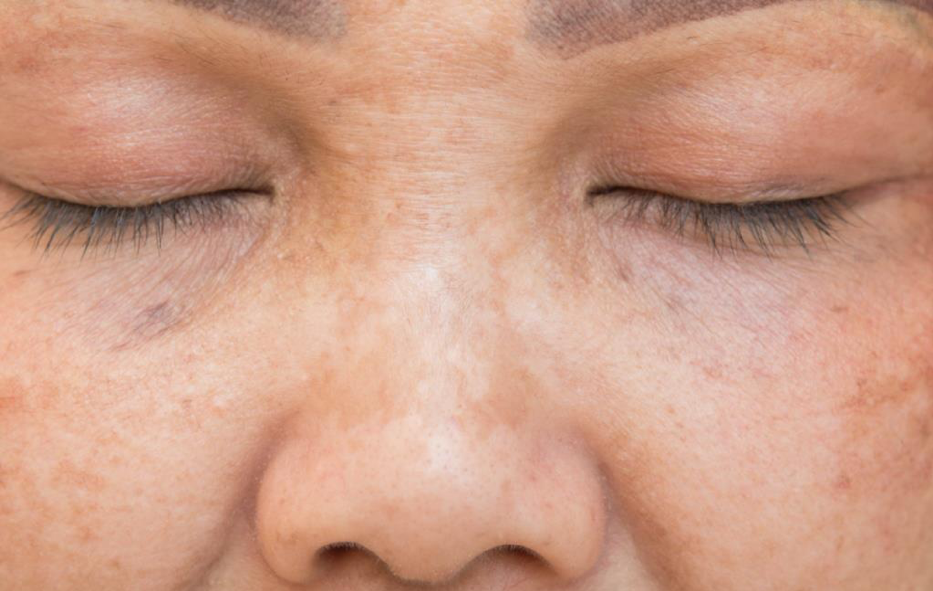
Even those of us who have dodged the worst that acne can throw at us avoided premature wrinkling, and been lucky enough not to fall prey to facial sagging can suffer from a telltale sign of ageing: age spots.
And little wonder: age spots, also known as sun spots or liver spots, are simply the body’s response to long-term overexposure to the sun. Over time, the body recognizes the sun’s UV radiation as a threat and produces extra melanin to protect itself from potential damage.
This response is gradual, and age spots typically present themselves most prominently starting in middle age, hence their popular name. These days, experts refer to the phenomenon as hyperpigmentation and have identified its three primary causes.
What causes hyperpigmentation?
Sun exposureis the leading cause of hyperpigmentation. A skin may tan or burn when first exposed to intense UV radiation from the sun, but extended intermittent exposure to sunlight triggers the production of extra melanin.
Pregnancycan cause a type of melasma known as a pregnancy mask, which appears as brownish patches on the face. It is caused by hormonal changes during pregnancy.
Traumato the skin can cause melanin to develop around the affected area. Acne scars and abrasions can cause melanin to gather around skin lesions, where it often stays even after the original injury has healed.
What treatments are available for hyperpigmentation?
Some cases of mild hyperpigmentation can be treated topically, with special creams and ointments. These can address age spots in various ways, but usually lighten the entire face, not just hyperpigmented areas. Problem areas tend to respond more dramatically to topical treatments than the surrounding skin. While topical treatments do not typically remove hyperpigmentation altogether, they can greatly diminish the contrast in skin tones that makes affected areas stand out.
More serious cases require clinical remediation. These procedures should be performed by trained experts, and some must be administered by licensed physicians. Some clinical therapies are nearly as gentle as topical treatments, and their effects just as subtle. Others actively seek out and destroy concentrations of melanin, and can completely eliminate hyperpigmentation, albeit at a much greater cost and with considerably more recovery time.
Topical treatments for hyperpigmentation
The two most common topical treatments for hyperpigmentation are exfoliation and skin lightening. Most clinics and spas can administer both.
Chemical or manual exfoliation removes layers of skin to encourage the regeneration of unaffected cells free of pigmentation issues.
Some topical treatments can bleach, brighten, or lighten selected areas of skin. Others lighten the skin overall. Hundreds of compounds claim to brighten skin, and dozens of ingredients claim to alleviate hyperpigmentation. Among the most popular nowadays are:
- Hydroquinoneinterrupts the skin’s ability to absorb and retain discolouration.
- Chromabright, also known as dimethylmethoxy chromanyl palmitate, has developed a reputation for gentle, effective, and safe skin lightening.
- Shiitake mushrooms,of all things, can lighten skin. They provide kojic acid, which brightens the skin overall, and may especially target unnaturally pigmented areas.
Clinical procedure for hyperpigmentation
When topical treatments don’t completely resolve pigmentation issues, clinical procedures can often help.
Laser skin treatmentcan be focused precisely on the layer of skin containing excess melanin. Because melanin absorbs light more readily than surrounding tissue, it receives the bulk of the laser’s energy. The laser breaks melanin molecules into smaller particles, which are then safely removed by the body’s natural processes. Lasers are often used to remove tattoos.If you’re interested in learning more about how lasers are used to remove all kinds of skin pigmentations, UbiqiHealth has published an in-depth article about pigmentation treatment in Singapore.
Microneedlingcreates tiny punctures in the skin, prompting the body to create new cells and to increase the rate at which existing cells are replaced. This can speed the process by which the body replaces cells affected by hyperpigmentation.
Chemical face peelsare among the most established clinical skin-care therapies. They work by carefully removing layers of skin cells, usually limited to the layer of dead cells that sits atop the skin. Among their benefits is a general lightening of the face; peels are often used in conjunction with other procedures when addressing hyperpigmentation.
Microderabrasionachieves the same benefits as face peels, but by mechanical means. A diamond-tipped stylus or a flurry of aluminium oxide crystals remove the targeted cells, while a vacuum pulls them away.
Experienced dermatologists should be ready to offer many or all of the services listed here. Every case of hyperpigmentation is different, and the right solution might involve a combination of several types of treatment.